Showing posts with label SE. Show all posts
Showing posts with label SE. Show all posts
Tuesday, August 14, 2012
SE 2008 Pattern Results are finally revealed : Pune University
Pune University has finally rolled out the results for SE 2008 pattern after a long wait. This time unusually SE results were declared after the FE, TE and BE results were declared. There were a lot of rumors spreading out about the results. The results which was supposed to be rolled out on 5th of August was again postponed for the 2nd time due to undisclosed reasons. But finally after a long wait, results have finally been given a Green signal.
Thursday, August 2, 2012
Free Educational App for learning PPS : [SE - Comp] [Sem 1]
Today we would like to bring to you a free and innovative Java based application for Learning the Subject : 'Programming & Problem Solving' - A Second Year, first Sem Computer Engineering Subject for Pune University. The app is a freeware and has been successfully tested by our team for malware and other problems. The app was contributed to us by one of our readers : Mr. Ajinkya Borle
There are a few details you need to know before you download and use the Application :
- The application is java based application and hence requires Java 1.6 or 1.7 to be installed on the user's computer.
- The Download Package contains a Setup file (.exe file) -which can be installed in the same simple and traditional way and an Instructions Manual(PDF) for user help.
- The software was made free of cost as it was sponsored by a Computer Shop named Swaroop Computers and hence the name 'Swaroop Computers' appears in the application as a part of the Sponsorship Program.
- The sponsor's website opens when the software is launched; this is neither a threat, malware, adware nor a spyware! It is only a part of the sponsorship deal with the application.
- The application is only distributed by IT Engg Portal and hence for any problems, queries and other help or information you are required to directly contact the developer : Mr. Ajinkya Borle ( Contact Information will be provided at the end of this post.)
Our team has tested the software and hence recommends all Second Year, Computer Engineering Students to utilize this application for studying the subject.
Here are a few screenshots of the Application.
Screenshot for Welcome Page (Splash Screen)
2. ScreenShot for Main page of the Application
For further details, you can contact the Contributor and Developer of this Application :
Mr. Ajinkya Shishir Borle
aborle@hotmail.com
Thursday, November 24, 2011
Waterfall Model - Software Engineering TE[Comp&IT] - Sem 5/ Sem 6
8:50 AM
Comp, IT, model, SE, Sem 5, Sem 6, software, Software Engineering, TE Pune University, waterfall, waterfall model
( Download as PDF )
Waterfall Model
Waterfall approach was first Process Model to be introduced and followed widely in Software Engineering to ensure success of the project. In "The Waterfall" approach, the whole process of software development is divided into separate process phases.
Overview
Waterfall development isn't new -- it's been around since 1970 -- but most developers still only have a vague idea of what it means. Essentially, it's a framework for software development in which development proceeds sequentially through a series of phases, starting with system requirements analysis and leading up to product release and maintenance . Feedback loops exist between each phase, so that as new information is uncovered or problems are discovered, it is possible to "go back" aphase and make appropriate modification. Progress "flows" from onestage to the next, much like the waterfall that gives the model its name.
Requirement Specifications phase
Software Design
Implementation
Testing
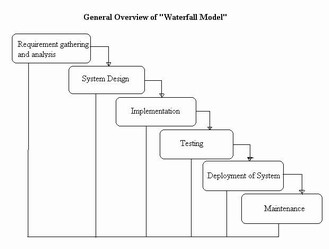
The stages of "The Waterfall Model" are:
Requirement Analysis & Definition:
Implementation
Testing
Deployment
Maintenance.
The stages of "The Waterfall Model" are:
Requirement Analysis & Definition:
All possible requirements of the system to be developed are captured in this phase. Requirements are set of functionalities and constraints that the end-user (who will be using the system) expects from the system. The requirements are gathered from the end-user by consultation, these requirements are analyzed for their validity and the possibility of incorporating the requirements in the system to be development is also studied. Finally, a Requirement Specification document is created which serves the purpose of guideline for the next phase of the model.
System & Software Design:
Before a starting for actual coding, it is highly important to understand what we are going to create and what it should look like? The requirement specifications from first phase are studied in this phase and system design is prepared. System Design helps in specifying hardware and system requirements and also helps in defining overall system architecture. The system design specifications serve as input for the next phase of the model.
Implementation & Unit Testing:
On receiving system design documents, the work is divided in modules/units and actual coding is started. The system is first developed in small programs called units, which are integrated in the next phase. Each unit is developed and tested for its functionality; this is referred to as Unit Testing. Unit testing mainly verifies if the modules/units meet their specifications.
Integration & System Testing:
As specified above, the system is first divided in units which are developed and tested for their functionalities. These units are integrated into a complete system during Integration phase and tested to check if all modules/units coordinate between each other and the system as a whole behaves as per the specifications. After successfully testing the software, it is delivered to the customer.
Operations & Maintenance:
This phase of "The Waterfall Model" is virtually never ending phase (Very long). Generally, problems with the system developed (which are not found during the development life cycle) come up after its practical use starts, so the issues related to the system are solved after deployment of the system. Not all the problems come in picture directly but they arise time to time and needs to be solved; hence this process is referred as Maintenance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
The waterfall model, as described above, offers numerousadvantages for software developers. First, the staged development cycleenforces discipline: every phase has a defined start and end point, andprogress can be conclusively identified (through the use of milestones) by bothvendor and client. The emphasis on requirements and design before writing asingle line of code ensures minimal wastage of time and effort and reduces therisk of schedule slippage, or of customer expectations not being met.
Getting the requirements and design out of the way firstalso improves quality; it's much easier to catch and correct possible flaws atthe design stage than at the testing stage, after all the components have beenintegrated and tracking down specific errors is more complex. Finally, becausethe first two phases end in the production of a formal specification, thewaterfall model can aid efficient knowledge transfer when team members aredispersed in different locations.
Disadvantages
Despite the seemingly obvious advantages, the waterfallmodel has come in for a fair share of criticism in recent times. The most prominent criticism revolves around the fact that very often, customers don'treally know what they want up-front; rather, what they want emerges out ofrepeated two-way interactions over the course of the project. In thissituation, the waterfall model, with its emphasis on up-front requirementscapture and design, is seen as somewhat unrealistic and unsuitable for thevagaries of the real world. Further, given the uncertain nature of customer needs, estimating time and costs with any degree of accuracy (as the model suggests) is often extremely difficult. In general, therefore, the model is recommended for use only in projects which are relatively stable and wherecustomer needs can be clearly identified at an early stage.
Another criticism revolves around the model's implicitassumption that designs can be feasibly translated into real products; this sometimes runs into roadblocks when developers actually begin implementation.Often, designs that look feasible on paper turn out to be expensive ordifficult in practice, requiring a re-design and hence destroying the clear distinctions between phases of the traditional waterfall model. Some criticism salso center on the fact that the waterfall model implies a clear division of labor between, say, "designers", "programmers" and"testers"; in reality, such a division of labor in most software firms is neither realistic nor efficient.
Customer needs
While the model does have critics, it still remains usefulfor certain types of projects and can, when properly implemented, produce significant cost and time savings. Whether you should use it or not dependslargely on how well you believe you understand your customer's needs, and howmuch volatility you expect in those needs as the project progresses. It's worth nothing that for more volatile projects, other frameworks exists for thinking about project management, notably the so-called spiral model...but that's a story for another day!
=======================================
Video Lectures
Overview of Different Models
Waterfall vs Agile
========================================
Wednesday, November 16, 2011
Pune University : SE [Comp & IT] Dec 2010 Question Papers
10:59 AM
Question Papers, SE, SE Pune University
Information Technology :
SE - 2010 Dec
|
Subject
|
Sem
|
Download
|
|
Discrete Structures
|
3
|
|
|
Computer Organization
|
3
|
|
|
Digital Electronics & Logic Design
|
3
|
|
|
Fundamentals of Data Structures
|
3
|
|
|
Humanities and Social Science
|
3
|
Computer Engineering :
SE - 2010 Dec
Subject
|
Sem
|
Download
|
Discrete Structures
|
3
| |
P.P.S
|
3
| |
Digital Electronics & Logic Design
|
3
| |
Data Structures & Algorithm
|
3
| |
Humanities and Social Science
|
3
|
|
Wednesday, October 26, 2011
WinRunner FAQ's & Viva questions
WinRunner - As a GUI based load testing tool
We use WinRunner as a load testing tool operating at the GUI layer as it allows
us to record and playback user actions from a vast variety of user applications
as if a real user had manually executed those actions. We use WinRunner in
addition to LoadRunner when we want to record user experience
response time. Visit
mercuryinteractive.com/products/WinRunner/ for detailed information on WinRunner.
The following diagram shows how a GUI layer testing tool, such as WinRunner, operates.
The WinRunner screen print shown below simulates a user starting up an
Internet Explorer session and connecting to
www.google.com.au before performing a
Google search on the text: "Mercury Interactive".
As can be seen, WinRunner records each
of the actions that the user performed on the desktop to get to and search the
Google web site.
This is in contrast to the way that VUGen
records the protocol that the client application generates. However, both tools
have their part to play in a load
test.
The screen image below is a script example of how WinRunner recorded the events on the windows
desktop to "Press Start" and then Invoke Internet Explorer by selecting the
option marked "Internet". The text "google.com" was recorded as
being entered as a URL and the "return" key (<kReturn>) was then recorded so the
IE loaded the Google site into the browser window. The characters "Mercury
Interactive" were then recorded as they were typed into the Google search field,
followed by another <kReturn> to initiate the search.
As can be seen from this script example, WinRunner does nothing at the protocol layer (like VUGen would) but records and plays back user
events, so that the underlying application operates as if a person was sitting
at the desktop.
For WinRunner to operate, it needs to be in control of the PC, so that it can
execute the user actions that had been previously recorded. This is why
one can not execute a load test
with WinRunner as the means of load generation. In order to simulate 100
users, one would need 100 PCs with WinRunner on each PC.
However, WinRunner is a valuable piece of load testing technology when used
properly in a load test as it is
the only means of determining the actual
user response time, taking into account
the processing that is executed on the clients hardware. (As
VUGen operates at a protocol level it is only able to
measure at a protocol level.)
Please visit performance
tests and network
sensitivity tests for other testing situations where it is very appropriate
to use WinRunner. By using WinRunner in these situations, WinRunner usage
will be extended beyond automated functional testing, increasing it's value to
your testing team and organization.
Download Ebooks:

Winrunner Viva Questions
Wednesday, October 5, 2011
Software Testing & Quality Assurance - BE [Comp / IT]
Software Testing & Quality Assurance is a very important subject introduced in the curriculum of Computer and IT Engineering. The subject has immense application in the industry and is a subject of huge importance to freshers and also to students from campus placement point of view. Freshers are normally asked to start their career in Software Testing in most of big Companies like Infosys, Accenture etc. Students who belong to branches other than Computer and IT are mostly given the profile of a Software Tester as a fresher (most of them).
Apart from curriculum, most of the companies do ask questions on Software Testing in the Technical Interview . The questions are mainly to analyze a students awareness about various software testing techniques. Companies like Cybage, Persistant, KPIT Cummins, Harbinger, Syntel and most other IT companies usually ask most of the questions on Software Testing in the Technical Interview.
Moving on to the syllabus, the subject is a bit vast and a bit confusing (since it covers huge amount of theory). The subject is scoring to certain extent, i mean scoring 65-70 is not a difficult task. The syllabus for Computer and IT Engineering is quite different and not the same.
# Note - Software Testing & Quality Assurance is a subject -
Syllabus for IT Engg :
Unit I Testing Principles
Need of testing, Basic concepts – errors, faults, defects, failures, test bed, unit testing, integration testing system, system testing, regression testing, alpha, beta and acceptance testing , functional testing, performance testing, recovery testing, white box testing, black box testing, verification and validation
Unit II Test Management
Testing Life Cycle – Roles and activities, Test Planning – forming a test team, develop test plan review
Test Cases design strategies black box approach: random testing, equivalence class partitioning and
boundary value analysis. white box approach: test adequacy criteria, coverage and control flow graphs,
paths, loop testing, mutation testing. Test execution: build test data, life cycle of defect, defect tracking, defect detection stages, defect detection stages, defect types, defect severity, defect analysis and prevention.
Unit III Software Metrics
Scope of software metrics, Classifying software measures, Measurement basics – representational theory, scales, meaningfulness, What to measure – GOM technique, Control flow structure, product quality metrics – MTTF, defect density, customer problems, customer satisfaction, function point, Metrics for software maintenance, In-process quality metrics.
Unit IV Quality Assurance
Quality concepts – quality, quality control, quality assurance, cost of quality Software quality assurance – SQA activities, software reviews, inspections, audits, Software reviews, inspections, audits, Software reliability Quality Attributes: correctness, reliability, usability, integrity, portability, maintainability, interoperability. Ishikawa’s Seven Basic Tools
Unit V Quality Standards
Basic concept of – ISO 9000 & 9001, CMM, six sigma.
Unit VI Development of CMM
CMM – Following KPAs : requirements management (RM), software project tracking and oversight (SPTO), software configuration management (SCM), organization process definition (OPD), software product engineering (SPE), peer reviews (PR), quantitative process management (QPM), defect prevention
(DP), process change management
Syllabus for Computer Engineering
Unit 1
Introduction, Basics of Software Testing, Testing Principles, Goals, Testing Life Cycle, Phases of Testing, Defects, Defect Life Cycle, Defect Report, Test Plan(IEEE format), Importance of testing in software production cycle.
Unit II
Introduction, Need of black box testing, Black box testing Concept, Requirement Analysis, Test case design criteria, Testing Methods, requirement based testing, Positive & negative testing, Boundary value analysis, Equivalence Partitioning class, state based or graph based, cause effect graph based, error guessing, documentation testing & domain testing, design of test cases. Case studies of Black-Box testing.
Unit III
Introduction, Need of white box testing, Testing types, Test adequacy criteria, static testing by humans, Structure - logic coverage criteria, Basis path testing, Graph metrics, Loop Testing, Data flow testing, Mutation Testing, Design of test cases. Testing of Object oriented systems, Challenges in White box testing, Case-study of White-Box testing
Unit IV
Test organization, Structure of testing, Measurement tools, Testing metrics: Type of metric – Project, Progress, Productivity, Metric plan, Goal Question metric model, Measurement in small & large system.
Other Software Testing: GUI testing, Validation testing, Regression testing, Scenario testing, Specification based testing, Adhoc testing, Sanity testing, Smoke testing, Random Testing. Advances in Software Testing Methods
Unit V
Software quality, Quality attribute, Quality Assurance, Quality control & assurance, Methods of quality management, Cost of quality, Quality management, Quality factor, Quality management & project management, Software quality metrics-TQM, Six Sigma, ISO, SQA Model.
Unit VI
Manual testing, Automated Testing Tools & Case studies, Study of Testing tools (QTP, Rational Robot, Winrunner, Loadrunner), Case studies based on Web based, GUI testing, Manual testing Vs Automated testing, Automated Testing Tools Case studies
Software Testing Interview Questions
(very Important - recommended for all)
===========================
=======================================================
Apart from curriculum, most of the companies do ask questions on Software Testing in the Technical Interview . The questions are mainly to analyze a students awareness about various software testing techniques. Companies like Cybage, Persistant, KPIT Cummins, Harbinger, Syntel and most other IT companies usually ask most of the questions on Software Testing in the Technical Interview.
Moving on to the syllabus, the subject is a bit vast and a bit confusing (since it covers huge amount of theory). The subject is scoring to certain extent, i mean scoring 65-70 is not a difficult task. The syllabus for Computer and IT Engineering is quite different and not the same.
# Note - Software Testing & Quality Assurance is a subject -
- Compulsory for IT Engineering (PU) [SEM 7]
- Elective for Computer Engineering (PU) [SEM 7]
Syllabus for IT Engg :
Unit I Testing Principles
Need of testing, Basic concepts – errors, faults, defects, failures, test bed, unit testing, integration testing system, system testing, regression testing, alpha, beta and acceptance testing , functional testing, performance testing, recovery testing, white box testing, black box testing, verification and validation
Unit II Test Management
Testing Life Cycle – Roles and activities, Test Planning – forming a test team, develop test plan review
Test Cases design strategies black box approach: random testing, equivalence class partitioning and
boundary value analysis. white box approach: test adequacy criteria, coverage and control flow graphs,
paths, loop testing, mutation testing. Test execution: build test data, life cycle of defect, defect tracking, defect detection stages, defect detection stages, defect types, defect severity, defect analysis and prevention.
Unit III Software Metrics
Scope of software metrics, Classifying software measures, Measurement basics – representational theory, scales, meaningfulness, What to measure – GOM technique, Control flow structure, product quality metrics – MTTF, defect density, customer problems, customer satisfaction, function point, Metrics for software maintenance, In-process quality metrics.
Unit IV Quality Assurance
Quality concepts – quality, quality control, quality assurance, cost of quality Software quality assurance – SQA activities, software reviews, inspections, audits, Software reviews, inspections, audits, Software reliability Quality Attributes: correctness, reliability, usability, integrity, portability, maintainability, interoperability. Ishikawa’s Seven Basic Tools
Unit V Quality Standards
Basic concept of – ISO 9000 & 9001, CMM, six sigma.
Unit VI Development of CMM
CMM – Following KPAs : requirements management (RM), software project tracking and oversight (SPTO), software configuration management (SCM), organization process definition (OPD), software product engineering (SPE), peer reviews (PR), quantitative process management (QPM), defect prevention
(DP), process change management
Syllabus for Computer Engineering
Unit 1
Introduction, Basics of Software Testing, Testing Principles, Goals, Testing Life Cycle, Phases of Testing, Defects, Defect Life Cycle, Defect Report, Test Plan(IEEE format), Importance of testing in software production cycle.
Unit II
Introduction, Need of black box testing, Black box testing Concept, Requirement Analysis, Test case design criteria, Testing Methods, requirement based testing, Positive & negative testing, Boundary value analysis, Equivalence Partitioning class, state based or graph based, cause effect graph based, error guessing, documentation testing & domain testing, design of test cases. Case studies of Black-Box testing.
Unit III
Introduction, Need of white box testing, Testing types, Test adequacy criteria, static testing by humans, Structure - logic coverage criteria, Basis path testing, Graph metrics, Loop Testing, Data flow testing, Mutation Testing, Design of test cases. Testing of Object oriented systems, Challenges in White box testing, Case-study of White-Box testing
Unit IV
Test organization, Structure of testing, Measurement tools, Testing metrics: Type of metric – Project, Progress, Productivity, Metric plan, Goal Question metric model, Measurement in small & large system.
Other Software Testing: GUI testing, Validation testing, Regression testing, Scenario testing, Specification based testing, Adhoc testing, Sanity testing, Smoke testing, Random Testing. Advances in Software Testing Methods
Unit V
Software quality, Quality attribute, Quality Assurance, Quality control & assurance, Methods of quality management, Cost of quality, Quality management, Quality factor, Quality management & project management, Software quality metrics-TQM, Six Sigma, ISO, SQA Model.
Unit VI
Manual testing, Automated Testing Tools & Case studies, Study of Testing tools (QTP, Rational Robot, Winrunner, Loadrunner), Case studies based on Web based, GUI testing, Manual testing Vs Automated testing, Automated Testing Tools Case studies
Books for Download
Practical Software Testing - Ilene Burnstein
(Recommended for IT )
Effective Methods for Software Testing
(Recommended for IT & Comp)
Software Testing Principles - Wiley Publications
Software Testing Interview Questions
(very Important - recommended for all)
Fundamental of Software Testing
===========================
Video Lectures :
Software Testing Interview Questions
--------
Why is Software Testing important??
-----------------
Bug Life Cycle
-------------------
Introduction to Software Testing & different types of Testing
--------
Manual and Automation Testing
---------
How to write a test case?
------------
Black Box Testing
White Box Testing
(part 1)
White Box Testing
(part 2)
White Box Testing
(part 3)
=======================================================
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)





























